Treating Gum Disease and Teaching patients on Prevention
Gingivitis and periodontitis
LANAP — or laser-assisted new attachment procedure — uses lasers to vaporize and remove diseased tissue from the mouth. First, the laser’s heat strips away the diseased gum. Then, the laser fires a second time to heat the area until a clot is formed, cauterizing the wound.
The PerioLase laser used in LANAP treats a range of conditions because its settings are easily adjusted and because the menu can be programmed for a specific procedure — haemostasis, implant surgeries (second-stage), biopsies, frenectomies and gingivectomies.
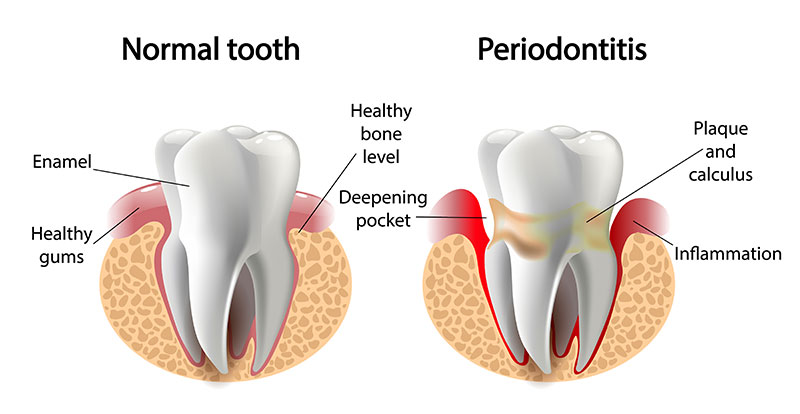
The two main gum diseases treated with LANAP are gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is sometimes termed non-destructive periodontal disease where patients experience inflammation and bleeding of the gums resulting from the buildup of plaque. Gingivitis can spread through bacterial infection to become periodontitis, causing the gums and bone structure in the mouth to deteriorate. The teeth may separate from the gums and surrounding bone structures through infected pockets containing tartar.
